FFA (Fundus Fluorescein Angiography)
- FFA can have adverse effects, including:
- Bluish color
- Cold, clammy skin
- Difficulty breathing
- Fast heartbeat
- Hives, itching, or skin rash
- Lightheadedness
- Noisy breathing
- Pain, redness, swelling, or peeling of the skin
- Your urine may look orange or dark yellow for up to 24 hours afterwards
- You may feel a burn on your skin if dye leaks during the injection
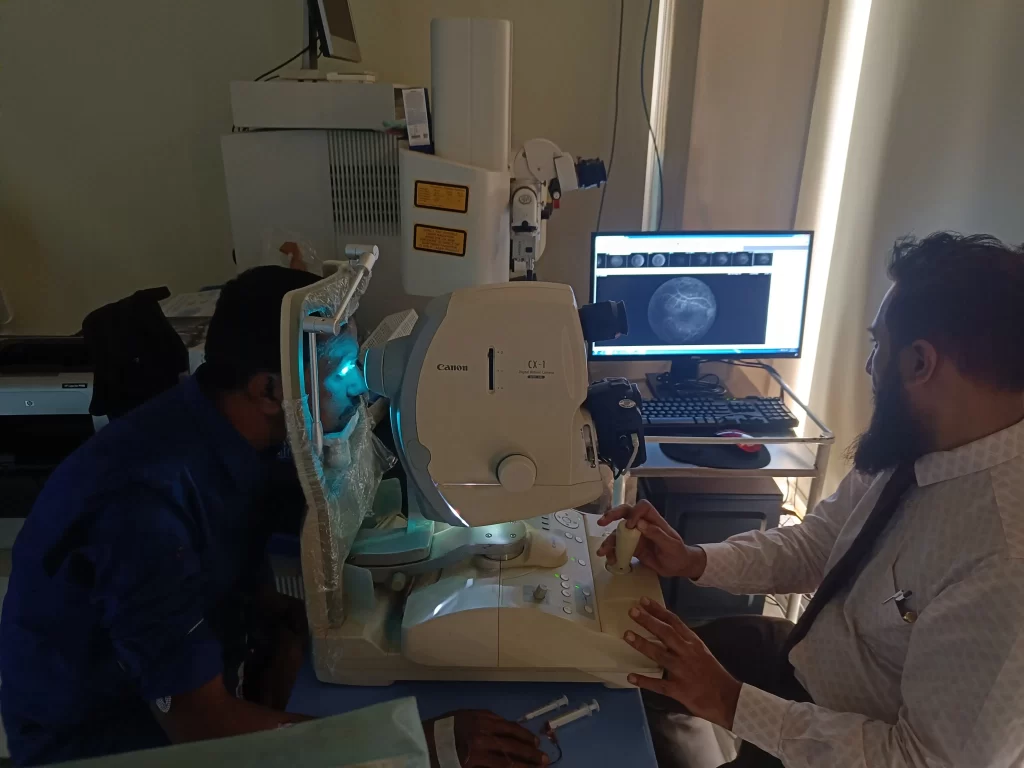
OCT Scan (Optical Coherence Tomography)
- OCT can be used in many different ways, including:
- Eye exams
- An optometrist may recommend an OCT exam if you're over 25 or at risk of developing eye disease. During the exam, you sit with your chin on a support and your eyes are scanned while you focus on a green target. You may notice a red line moving across your vision. OCT can help diagnose eye diseases such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD), glaucoma, diabetic retinopathy, macular hole, macular pucker, macular edema, central serous retinopathy, and vitreous traction.
- Coronary artery examinations
- OCT can be used to examine the coronary arteries and has 10-fold higher resolution than intravascular ultrasound (IVUS).
PERIMETRY
- Perimetry, also known as campimetry, is a diagnostic tool that measures the visual field
- It's used to assess glaucomaoptic neuropathies and other conditions that affect the visual pathway. Perimetry can also help monitor the progression of diseases and guide treatment.
During a perimetry test, you sit in a bowl-shaped instrument called a perimeter and look inside. While you stare at the center of the bowl, lights flash, and you press a button each time you see a flash. The test measures all areas of your eyesight, including your peripheral vision.
The two most common types of perimetry are Goldmann kinetic perimetry and threshold static automated perimetry.
In a visual field test, sensitivity normally decreases gradually with age. Positive values represent areas of the field where the patient can see dimmer stimuli than the average individual of that age. Negative values represent decreased sensitivity from normal.
Most patients have field testing once a year. If a change is seen, the field is repeated within 1 to 3 months, depending on the likelihood of the change being real and the amount of disease.




